Overview of Payment Bank License in India
The notion of Payment Bank has gotten both outstanding and reaching hooks in its banking circle industry in the recent era. Payment Bank refers to a recently created RBI model that accelerates transactions, similar to a traditional bank, with the exception of issuing credit cards and lending. To launch an online Payment Bank in India, a firm or an NBFC must first obtain a Payment Bank License from the Reserve Bank of India.
Furthermore, the concept of a Payment Bank has gained a lot of traction because it has the power to provide extensions to the government's financial targets. It should also be highlighted that the concept of demonetization dramatically transformed the Indian economy. As a result, individuals are relying more on digital payment gateways and paperless transactions, which has boosted the popularity of E-wallets and Mobile Wallets, which were previously overlooked.
Payment Banks: Laws Governing the Concept
The Reserve Bank of India first proposed the concept of a specialised bank model in 2013. Payments Bank was the name given to the institution. It should be mentioned that, like other Banks, a Payment Bank offers a variety of financial services, with the exception of credit cards and loan facilitation. The applicant organisation must receive a Payment Bank License from the Apex Bank in order to operate a Payment Bank in India.
In addition, the Reserve Bank of India will grant the applicant company a Payment Bank License under Section 22 of the Banking Regulations Act 1949. The applicant is permitted to engage in banking activities under the terms of the licence. The phrase "banking activities" has the same meaning as it does under the Banking Regulation Act's section 5 (b) and 6 (1) (a) to (o) provisions.
Payment Bank License Regulatory Structure
The following is the regulatory structure for a Payment Bank License:
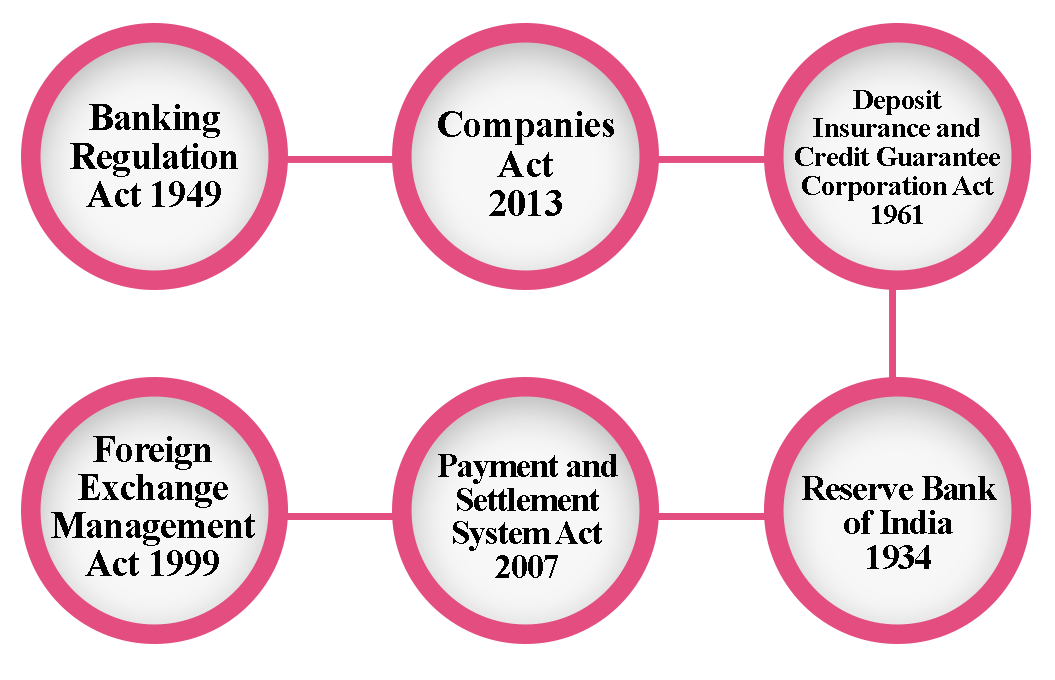
- Banking Regulation Act 1949.
- Companies Act 2013.
- Deposit Insurance & Credit Guarantee Corporation Act 1961.
- Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999.
- Payment & Settlement System Act 2007.
- Reserve Bank of India 1934.
Payment Bank in India's Objectives
The main goal of establishing a Payment Bank in India was to expand the reach and scope of payment services to small enterprises and low-income people. Furthermore, the Reserve Bank of India wants to boost financial penetration into distant areas by using the Payment Bank concept. The Bharti Airtel Payment Bank was India's first payment institution.
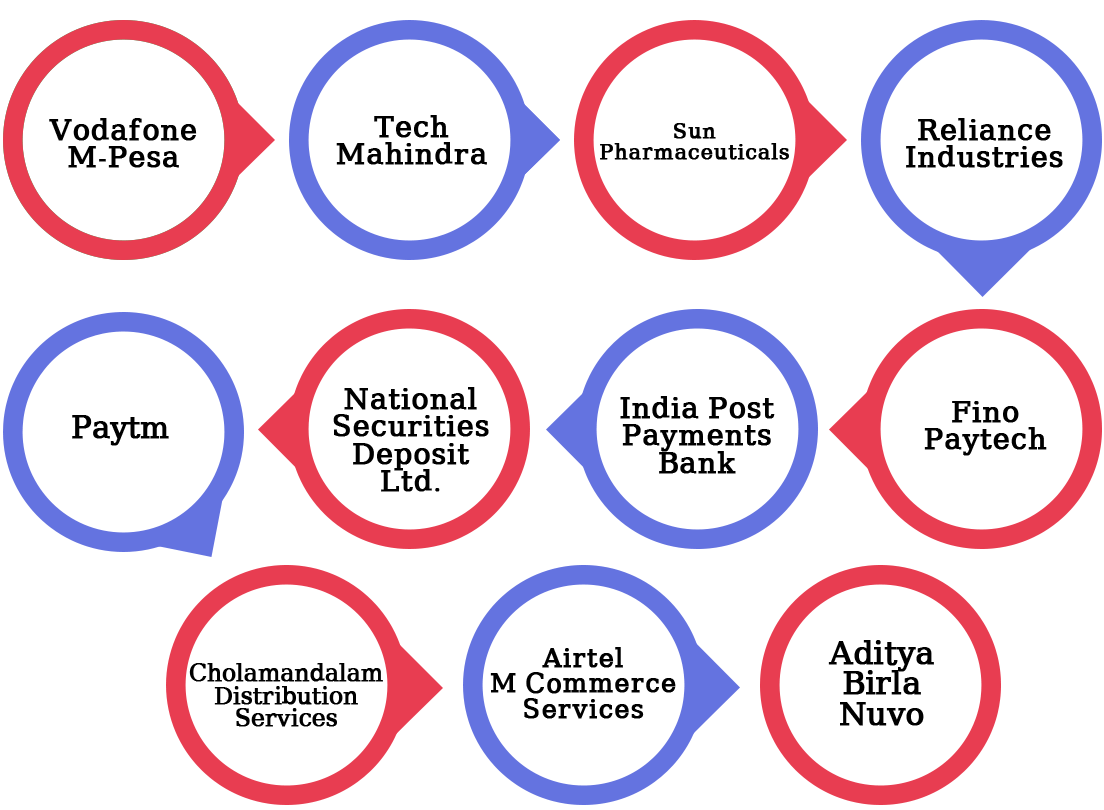
In addition, the following is a full list of Payment Banks that operate in India:
Key Benefits of the Payment Bank License in India
The following are the main advantages of obtaining a Payment Bank License in India:

Zero Balance Account
One of the major advantages of a payment bank is that the account holder is not forced to maintain a certain amount as the minimum needed amount. That means that a person's account balance can be zero.
Increased Interest Rates
The cost savings resulting from operational efficiency are passed on to the client in the form of increased interest.
Convenience
Another important advantage of a Payment Bank is that, thanks to its extensive distribution network, telecom service providers and mobile wallets can turn their retail locations into distinct banking sites.
Secure and Safe
The Reserve Bank of India developed the concept of a payment bank as one of the secure forms of online transaction due to 4 factor authentications.
Account Number and the Mobile Number are Same
Normally, this is a minor feature, but it improves the level of convenience for cardholders, particularly small business traders, merchants, and others, because they do not need to remember any other number like an account number to conduct transactions.
Offers for Cashback and Discounts
A payment bank, like any other mobile wallet, provides the customer with a variety of discount and rebate incentives.
Additional Advantages
Aside from reward and discount offers, a Payment Bank provides a variety of perks to its account customers.
Payment Bank Characteristics in India
The following are the basic qualities of an Indian Payment Bank:
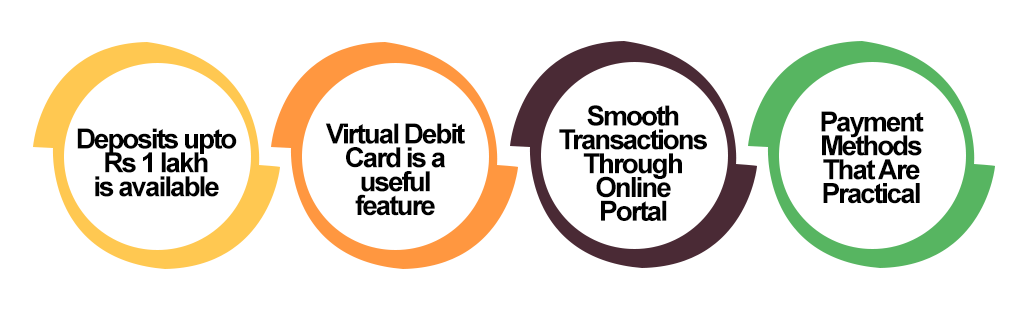
Deposits up to Rs 1 lakh are available
A payment bank can take deposits of up to Rs 1 lakh. Customers must adhere to the stipulated limit at all times, and no one is permitted to exceed it at any time. It should also be mentioned that an individual might choose to deposit an amount in full or in part.
In light of the relatively new nature of such institutions, the Reserve Bank of India has set a restriction to protect and preserve customers' interests.
Virtual Debit Card is a useful feature
Another unique feature of the payments bank is that it allows users to use both physical and virtual debit cards. Furthermore, debit cards give clients the ability to use any ATM (Automated Teller Machine) within the United States and overseas. The use of virtual debit cards does not include any additional fees for cash withdrawals. Furthermore, the physical debit cards are only supplied by a one-time annual cost.
Smooth Transactions Through Online Portal
In contrast to traditional banks, the concept of payment banks simplifies the process of sending and receiving money via digital channels. It also provides consumers with online fund transfer services such as NIFT, IMPS, and others.
Payment Methods That Are Practical
Because payment banks operate online, everyone, regardless of where they live or where they are located, can readily use their services. A payment bank eliminates the need to visit a real bank to deposit or withdraw money.
It should also be emphasised that anyone can start a payments bank business online, even if they don't have a physical location. The Payment Bank License is the only requirement.
Who is eligible to apply for a Payment Bank License in India?
The following individuals are eligible to apply for a Payment Bank License in India:
- Individuals or professionals.
- Companies that provide mobile phones.
- Non-Banking Financial Institution (NBFC).
- Cooperatives in the Real Estate Sector.
- Supermarket franchises.
- Entities in the Public Sector.
- A Promoter or a Group of Promoters who owns a Joint Venture with a Scheduled Commercial Bank that is already in existence.
- The Payment & Settlement Systems Act of 2007 regulates non-bank PPIs (Prepaid Payment Instruments).
- Correspondence between companies.
- Companies that are publicly traded.
Capital Requirements in India for Obtaining a Payment Bank License
The following are the capital requirements for obtaining a Payment Bank License in India:
- To begin payment in India, the applicant company must have a minimum paid-up equity of Rs 100 crore.
- A payment bank must have a minimum CAR (Capital Adequacy Ratio) of 15% of its total RWA in India (Risk Weighted Assets). The same is subject to any additional amounts that the RBI may specify from time to time.
- At least 7.5 percent of total Risk Weighted Assets must be in Tier I Capital.
- Tier II Capital should be limited to no more than 100 percent of Tier I Capital.
- A Payment Bank is not permitted to handle complex items. The Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is calculated using the Basel Committee's Standardized Approaches.
Information to be provided to the Reserve Bank of India
The following information must be sent to the Reserve Bank of India:
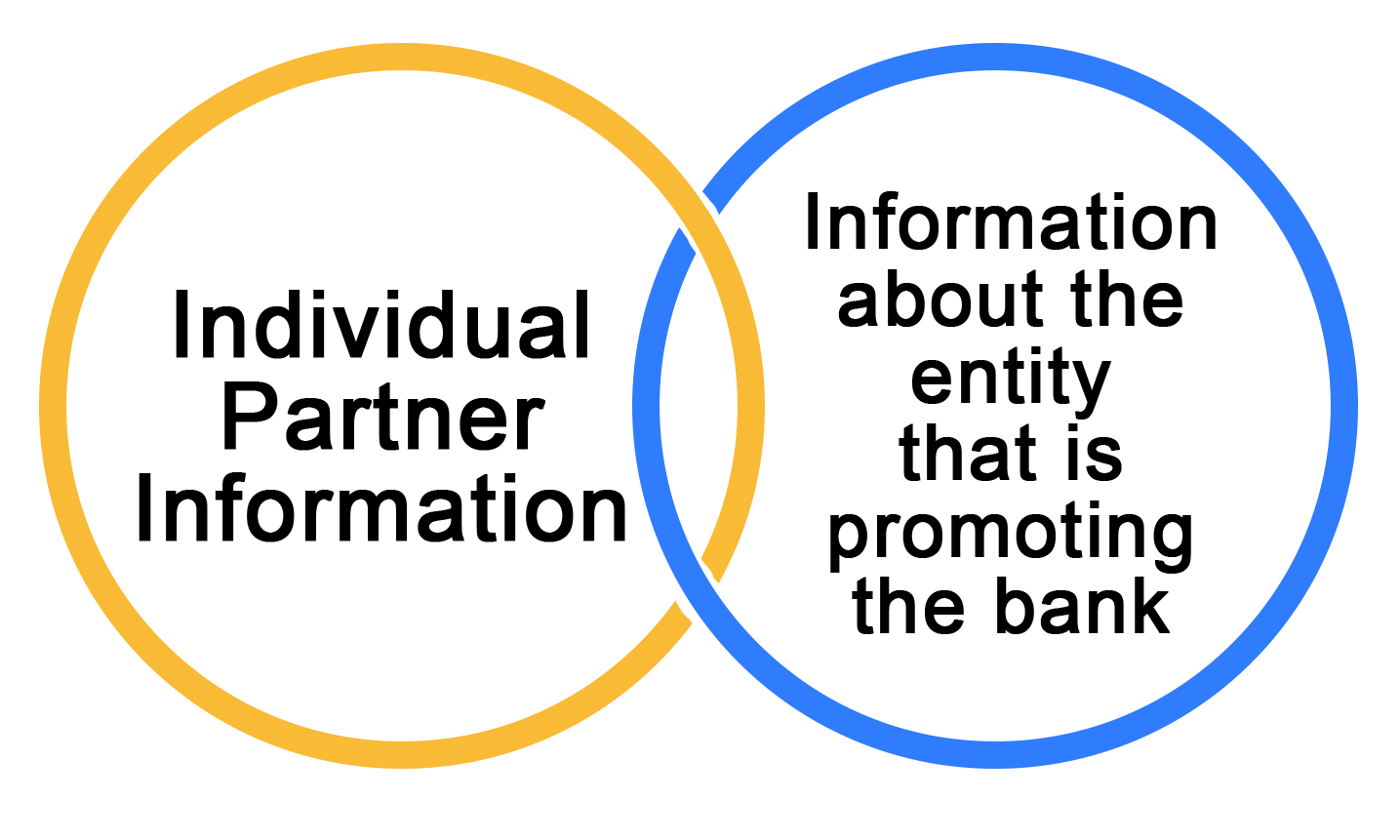
Individual Partner Information
The following information is requested from the Individual Partner:
- The promoter's name
- of PAN (Permanent Account Number)
- The partner's date of birth.
- The Promoter's Personal Experience
- Status as a resident.
- Details about the parents.
- Details about the branch
- Details about your current bank account, as well as your credit facilities.
- Expertise in various fields.
- The company's track record, as well as its financial worth.
Information about the entity that is promoting the bank
The following information is required from the Entity Promoting the Bank:
- The Entity Promoting the Bank's Shareholding Pattern
- The Entity Promoting the Bank's Memorandum of Association (MOA).
- The Entity Promoting the Bank's Articles of Association (AOA).
- Financial Statements of the entity promoting the bank for the preceding five financial years.
- ITRs (Income Tax Returns) from the past three fiscal years.
Common Details for both Entity Promoting the Bank and Individual Partner
- Names of all the Individual Partners and Entities operating in the Promoter Group
- The current Shareholding Pattern is described in detail.
- Organogram with pictures.
- Management information.
- The entities' total assets and liabilities.
- Financial Statements for the Previous Five Years
- Details of the RSE's Listing Shares (Recognized Stock Exchanges).
- Details on the PAN (Permanent Account Number).
- Account Number for Tax Deduction and Collection.
- Number assigned to a company.
- Details of your bank account
- Information about the bank branch.
Activities Permitted by Obtaining Payment Bank License in India
The following activities are permitted by acquiring a payment bank licence in India:
- A Payment Bank is allowed to take deposits up to a certain amount. Furthermore, the term "deposits" encompasses both current deposits made by small-scale merchants and individual savings bank deposits.
- Non-resident individuals (NRIs) are not permitted to make any deposits in Payment Banks.
- Customers of a Payment Bank are eligible to receive ATM or Debit Cards.
- Payment banks are not permitted to participate in lending activities.
- A Payments Bank, like any other bank, must conduct its own Know Your Customer (KYC)/Anti Money Laundering (AMT)/Combating Financial Terrorism (CFT) exercise.
- A payment bank is not permitted to provide loan and visa administration services in India.
- A Payment Bank can provide payments and remittance services through ATMs, Business Correspondents, and mobile banking. It should also be mentioned that remittance and payment services may include the acceptance of funds at one end through various channels such as branches and BCs, as well as cash payments at the other end.
- The Payment and Settlement Instrument Act of 2007 requires a Payment Bank to issue Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs) in compliance with the instructions provided.
- Based on the RBI's standards, a Payment Bank is eligible to provide Internet Banking Services; a Payment Bank is also eligible to become a Business Correspondent of another bank.
- A Payment Bank can take remittances from scheduled banks using a payment mechanism approved by the Reserve Bank of India, such as RTGS/NEFT/IMPS.
- Cross Border Remittance Transactions in the form of personal remittances are allowed to be handled by a Payment Bank.
- Payment Banks are not permitted to form subsidiaries to carry out the activities and operations of a non-bank financial institution (NBFI).
- Payment banks are permitted to pay utility bills on behalf of their customers as well as the general public.
- Other non-risk-sharing simple financial services operations are permissible for a Payment Bank, but only with RBI clearance. It also has to meet the regulatory sector's standards for such products.
Process for obtaining a Payment Bank License
The following are the steps involved in acquiring a Payment Bank License:
- The applicant must first register a Public Limited Company under the terms of the Companies Act 2013.
- Now, submit an application to the Apex Bank's CGM (Chief General Manager) for authorization to obtain a Payment Bank License.
- The EAC (External Advisory Committee) is then tasked with evaluating the submitted application. The applicant must then be summoned to verify the information provided by them.
- If the application company meets all of the requirements, the RBI will grant a Payment Bank License.
- Following the final phase, the applicant's name will be published on the RBI's official website.
- Finally, after receiving Apex Bank's primary approval to operate as a payment bank, the applicant company must form a bank within 18 months of the license's issue.
Why Choose Us

Free Legal Advice

Transparent Pricing
On Time Delivery
Expert Team

Money Back Guarantee

200+ CA/CS Assisted

Lowest Fees

Easy EMIs
Frequently Asked Questions
A payment bank's major goal is to ensure financial inclusion by providing remittance and payment services to underserved groups.
The payments bank's main focus is on boosting the migrant labour force, launching modest savings accounts for small business owners, and assisting unorganized sector employees and low-income people.
 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325











