Brief of Indian Subsidiary Company Registration
Due to growing opportunities, foreign investors are investing more in India, as a result, the level of FDI is booming at a great pace. Also, with the implementation of Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999, investing money in India has become much easier and more straightforward in nature. Therefore, the RBI has introduced different set of rules for the formation and incorporation of Indian Subsidiary Company.
Concept of Indian Subsidiary Company
As per the provisions of section 2(87) of the Companies Act 2013, a subsidiary company is considered as a company that is controlled by some other company. In short, to understand subsidiary company, there is a need to understand the concept of Holding Company.
Further, the term “Holding Company” is defined under the provisions of section 2 (46) of the Companies Act 2013. As per this section, a holding company means an entity in which controls of more than 50% stake are with some other company. Therefore, if the control and management of a company with another company, then the latter company is termed as a holding company.
Moreover, the term “Indian Subsidiary Company” has been defined under the provisions of the Companies Act 2013, according to which a company that is controlled by a foreign company (having stake of 50% or mor in paid-up capital) is known as an Indian subsidiary company.
Status of Indian Subsidiary Company
In terms of status, the principal of “Separate Legal Entity” will apply to a Indian subsidiary company as well. Therefore, the status of the directors and shareholders of the subsidiary is different and distinct from that of the corporate entity.
Further, as per the provisions of the Companies Act 2013, an Indian subsidiary company can be registered either as a public limited company or a private limited company.
Recent Amendments in FDI Policy
As per the recent amendments made by the government in FDI Policy in April 2020, the countries that share land borders with India now need government approval prior to investing in India.
Further, in total 7 countries share their border with India. That means these countries require prior approval from the competent regulatory authorities according to statutory laws to set up subsidiary companies in India.
Regulatory Authority for Indian Subsidiary Company
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs or MCA is the primary regulatory authority for the registration of an Indian Subsidiary Company. Besides this, the Registrar of Companies or ROC is responsible to handle all matters concerning the incorporation of an Indian subsidiary company.
Further, the other regulatory authority that is responsible for administering the affairs of an Indian Subsidiary Company is the Reserve Bank of India.
Benefits of Indian Subsidiary Company
The benefits of Indian Subsidiary Company are as follows:
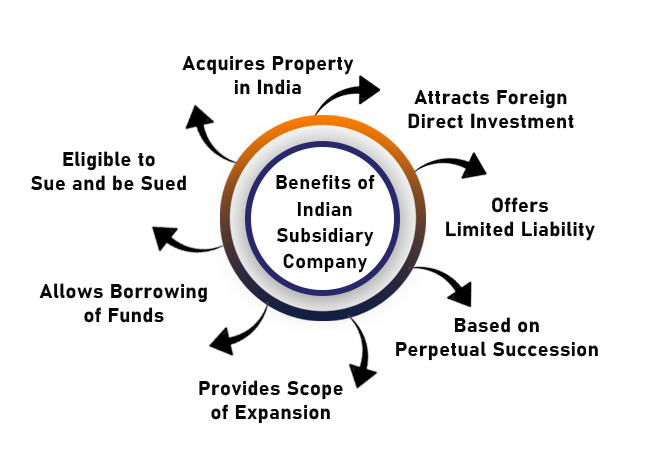
Attracts Foreign Direct Investment
For promoting the faster growth of industries, the Indian government has approved 100 percent involvement of FDI (Foreign Direct Investment). That means FDI is allowed 100 percent without any previous approval.
However, if the applicant has either a Partnership Firm, Sole Proprietorship or LLP then he/ she needs to obtain prior approval from the central government for FDI.
Offers Limited Liability
The term limited liability means that the members of an Indian subsidiary company will be liable till the extend of shares held by them. That means they will not be liable to use their personal assets for disposing off company’s liabilities.
Based on Perpetual Succession
The term “Perpetual Succession” means that in the event of insolvency, change in number of members, transfer, or death of members or directors, the company will continue to exist.
Provides Scope of Expansion
An Indian Subsidiary Company has all the privileges and benefits that of a Private Limited Company. That means the growth and expansion of a business is much easier in an Indian Subsidiary Company as it raises capital from various sources, such as financial institutions, venture capitalist, and investors.
Allows Borrowing of Funds
A fully-owned Indian subsidiary company enjoys the benefit of borrowing funds, in form of loans from the financial institutions.
Eligible to Sue and be Sued
Just like any other corporate entity, the Indian subsidiary company is a legal person as well. That means it has the power to sue and can get sued as well.
Acquires Property in India
A Foreign subsidiary company operates as an independent business structure which gives them the right to buy properties in India.
Documents Required for the Incorporation of an Indian Subsidiary Company
The documents required for the incorporation of an Indian Subsidiary Company are as follows:
For an Indian National
- PAN Card;
- Address Proof in the form of house tax receipt, utility bill, etc;
- Identity Proof in the form of an Aadhaar Card, Driving License, Passport, Voter Id;
For a Foreign National
- Passport;
- Address Proof (the same must be certified by Indian Consulate);
- Identity Proof (the same must be certified by Indian Consulate);
Other Significant Documents
- Directors Identification Number (DIN) for all the directors;
- Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) for at least one director;
- A copy of Memorandum of Association (MOA);
- A copy of Article of Association (AOA);
- No Objection Certificate (NOC) from the person who owns the premise being used as business place;
- Certificate of Incorporation (COI) issued by the foreign government;
- Residential Proof of all the directors;
Process to Register Indian Subsidiary Company
The steps involved in the process to register an Indian Subsidiary Company are as follows:

Apply for Name Approval
The first step in the process of registration is to obtain Name Approval from the MCA (Ministry of Corporate Affairs) name proposed. Further, it shall be considerate to note that the names proposed must be unique in nature and should not include any name that is offensive and prohibited by the government.
Apply for DSC and DIN
Now, it is mandatory for all the proposed directors to have DIN (Directors Identification Number) and out of all the directors at least one director should have DSC (Digital Signature Certificate) to sign documents electronically.
Apply for PAN and TAN
In the next step, the directors require to apply for company’s PAN (Permanent Account Number) and TAN (Tax Account Identification Number), as these are one of the compulsory requirements for incorporating any company in India.
Open a Bank Account in Company’s Name
After that an Indian Subsidiary Company needs to open a bank account, as the same is required for carrying out business transaction on behalf of the company.
Obtain GST Number
It is mandatory for all the Indian Subsidiary Companies incorporated in India to obtain GST Registration for carrying out operations.
Start Business Operations
Once the above-mentioned steps of the procedure for registration is complete, the India Subsidiary Company can start carrying out its business operations.
Biz Process

Free Legal Advice

Transparent Pricing
On Time Delivery
Expert Team

Money Back Guarantee

200+ CA/CS Assisted

Lowest Fees

Easy EMIs
Frequently Asked Questions
As per the provisions of the Companies Act 2013, the control over percentage for an Indian Subsidiary Company is 50%.
Yes, a Private Limited Company can be formed for incorporating Indian Subsidiary Company.
 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325











