Overview of Income Tax Return Filing
Income Tax Return Filing is a form or document that calculates assessed income earned in a year and the amount of taxes to be paid by him/her to the government or government organizations. Income tax is treated as an annual tax. The information filed in the income tax return should be of the particular financial year i.e. from 1st April to 31st March. The income tax return is filed on the previous year in the assessment year on the rates applicable in the assessment year. The tax rates are managed by the Annual Finance Act.
Basis of Charge for Income Tax Liability
An assessee earns his income in India or outside India or at both places. But which income is assessable in India depends on the residential status of an assessee. The total income of an assessee along with his residential status is based on his residence in India in the previous year. Residence and citizenship are two different aspects. The incidence of income tax liability has nothing to do with citizenship. An Indian may be a nonresident and a foreigner may be a resident for income tax purposes in India. On the basis of residence, the assessees are divided into three categories as mentioned below:
- The Ordinary Resident
- Not Ordinary Resident
- Non Resident
Heads of Income
All kinds of taxable income of an assessee fall under any of the following five heads of income. To calculate the taxable income, certain deductions are to be made under each head from the gross income of that head. The deductions are different for each head and have their separate conditions to be fulfilled. The different heads of income are given below-
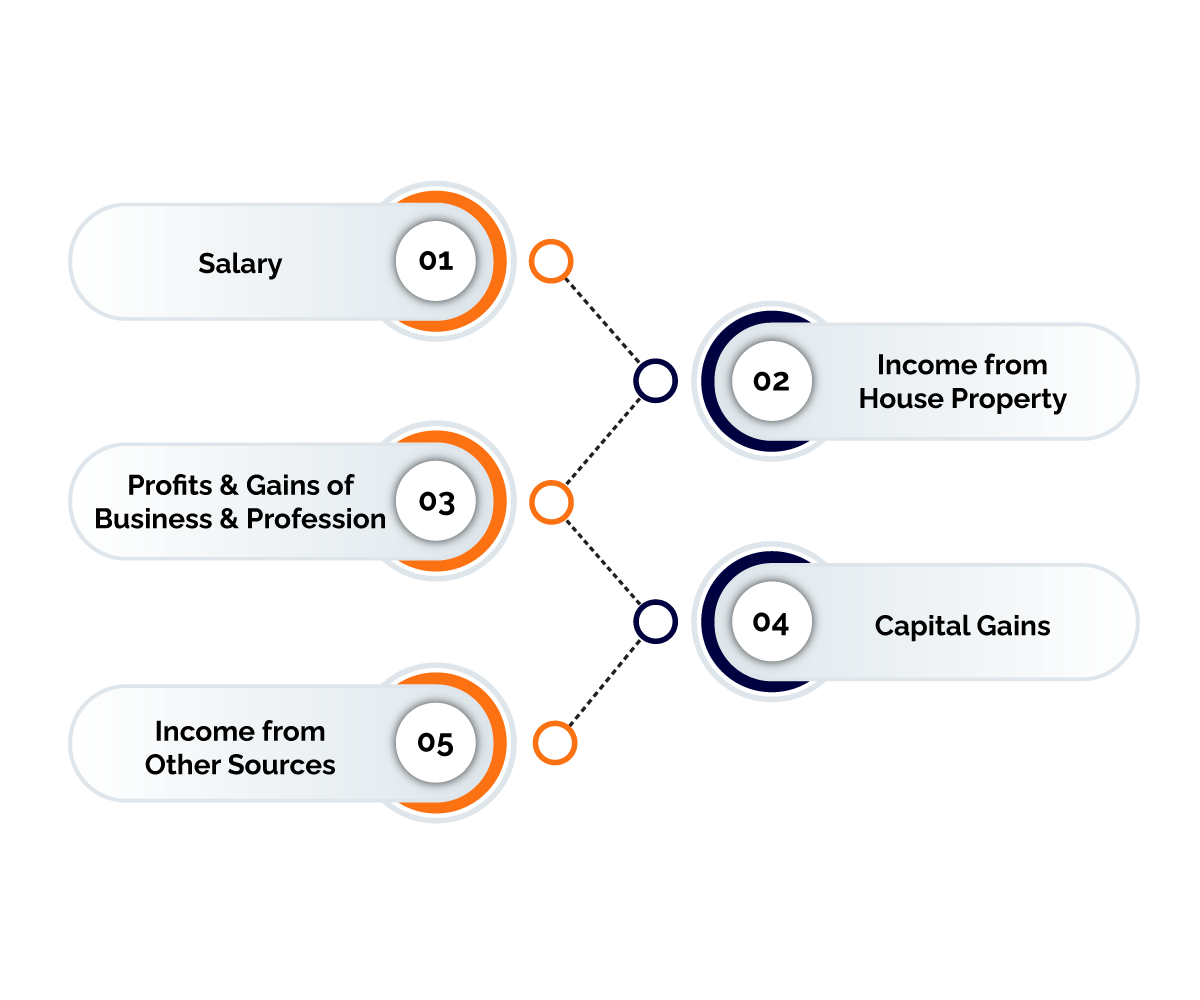
- Salaries- Any remuneration paid by an employer to his employee in consideration of his/her services is salary. If the relationship of employer and employee is present in the transactions thus the income would be said as income from salary.
- Income from House Property- This clause sheds light on the taxation policy on the house property of an individual. When any taxpayer owns more than a single self-occupied house, only one is considered self-occupied and the rest are considered to be let out. The tax amount is not based on the amount of the rent but rather on the property or land as a whole. For income from house property to be taxable, there are certain conditions that must be fulfilled. The first condition is the house property consists of any building or lands appurtenant thereto, the second is the assessee is the owner, and the last one is the house property must not be used for purposes of the assessee's business or profession.
- Profits and Gains of Business or Profession- This is the third head under the basis of charge. Business means the purchase and sale or manufacture of a commodity with a view to earning profit. It includes any trade, commerce, or manufacture. Whereas, Profession is the activities for earning livelihood which requires intellectual skills or manual skills, e.g., the work of a lawyer, doctor, auditor, engineer, and so on. The profession includes vocation. Under this head, the profits and gains made during the tenure of business or profession are subject to complete and total taxation. The incomes chargeable as Income Tax are the revenue profits from business or profession, income of trade association, interest on securities, the value of any benefit or perquisite, and the income from speculative transactions.
- Capital Gains-The basis of charge in Capital Gain is the profit or gains arising from the transfer of a capital asset in the previous year, it can be movable or immovable, and deemed taxable under the head Capital Gain. The essential elements of capital gains are a capital asset, transfer of a capital asset, and computation of capital gain.
- Income from Other Sources- The last head of income under the Income Tax Act is income from other sources. Any income which is derived from any other source other than the above-mentioned four heads will be considered to be under this category of heads. Incomes that are chargeable under the head income from other sources to income tax are dividends, income from winning lotteries, crossword puzzles, races, gambling or betting or any other with the same nature, interest on securities, income from letting of machinery, plant, or furniture and also the income received under a Key man insurance policy.
Benefits of Income Tax Return Filing
The following are the benefits of Income Tax Return Filing-
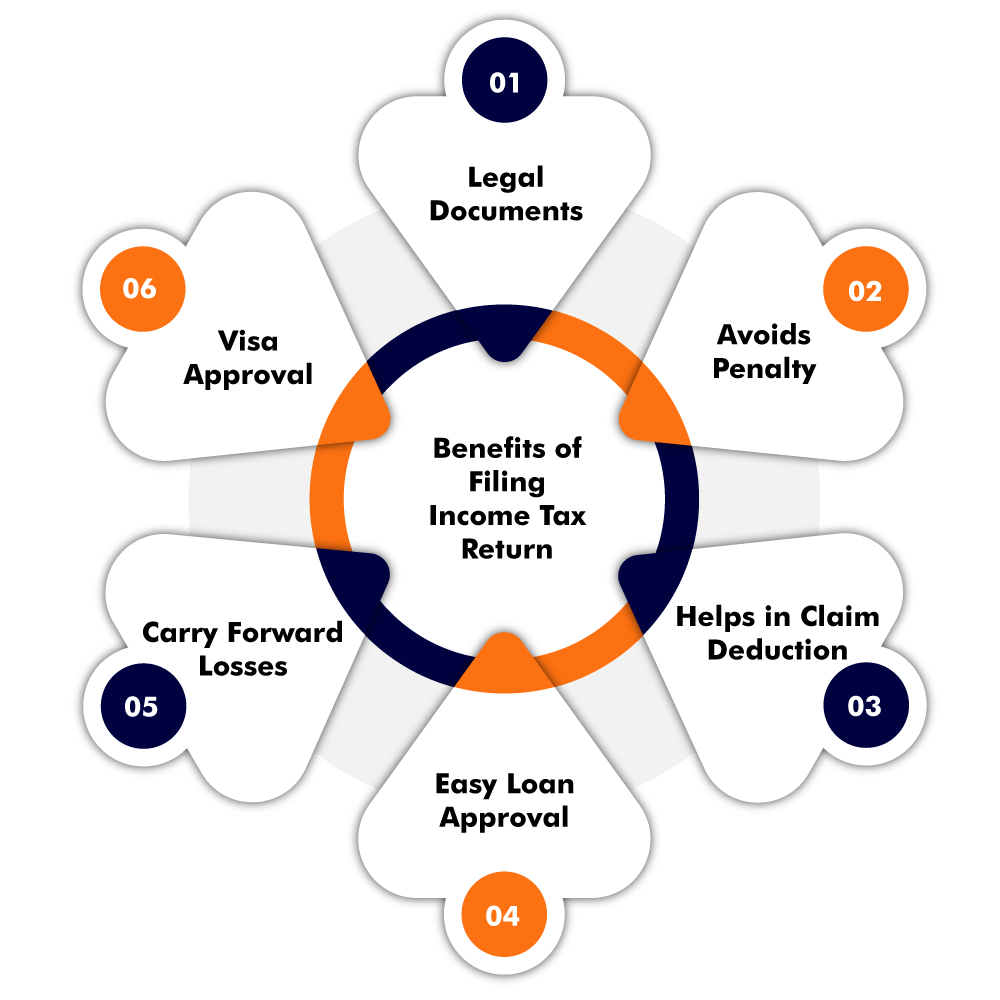
- Claim Deductions
To encourage more and more taxpayers to pay their taxes on time and to reduce the burden on taxpayers, the government has provided certain deductions such as TDS and Rebates of Income Tax can be claimed back, and also the deductions and exemptions can be used in some investments and thus helps in tax reduction ultimately.
- Easy Loan Approval
Applying for the loan proceeds to purchase something either for self or the family or the business, the bank requires certain documents to be submitted such as an Aadhar card, PAN card, etc. And banks also ask for the ITR proof of the last three financial years. This document is required to access the situation that one will be able to pay back the loan or not.
- Legal Document
The Income Tax Return Filing acts as a legal document for an individual as it gets recorded with the Government of India and thus holds immense legal value. It acts as legal proof for identity proof as well as income proof.
- Easy Visa Processing
Applying for a Visa involves some procedures to be followed up. Filing from time to time ITR is one of those required essential documents for processing visas for different countries. As if ITR is not filed by the due date, it can hurdle the plans for abroad.
Filing ITR on time helps an individual to show up his case and makes chances of getting visa approval. It provides the details of the financial situation of the individual to the embassy.
- Avoids Penalty
The taxes which are imposed on the taxpayers are governed by the Income Tax Act, 1961. Thus every assessee is compelled to pay taxes if he/she falls under certain criteria. Thus if an individual is eligible to pay tax on his income earned and fails to file ITR, then the penalty is imposed on the taxpayer. Thus, one should file ITR on due time to be safe from penalties and punishments.
- Losses can be Carried, Forward
year. Such as the loss from the head income from house property can be carried forward and set off till a maximum of eight assessment years from the income of house property and carry forward loss of specified business shall be set off from the profits and gains. This loss can be carried forward and set off till it is fully set off.
Forms Related to Income Tax Return Filing
The Income Tax Act has described seven types of Income Tax Return Filing Forms. The applicability depends on the very nature of the income and the type of the taxpayer. The list of Income Tax Return Filing Forms is given below-
ITR-1 Form
ITR-1 Form is also well known as the Sahaj form. Individual taxpayers choose this form to file their returns and no other taxpayers are allowed to choose this form for Income Tax Return Filing. An individual whose income arises from salary or pension or whose income is fully dependent on the single housing property or where the individual’s income is without capital gains and other business can use this form. The agricultural income of an Individual up to Rs.5000 can also use this form. Individuals whose income exceeds Rs.50 lakhs or whose agriculture income exceeds Rs.5000 or he/she earns income from more than one house properties or non-residents and residents not ordinarily residents are not eligible for the above mention Income Tax Return Filing Form.
ITR-2 Form
This form can be filed by the partners in a firm where no business is conducted. It includes Individuals and HUFs. The above mention form can be used by an individual whose income is from the partnership in a firm or he/she is a company director or where any business or profession is being followed by an individual or any income arising from house property, pension, salary, or other sources. It excludes individuals whose business turnover is below Rs. 2 crores or where the income doesn’t arise from a business conducted by a firm or in case the Taxpayers income arises from the business in the form of salary, bonus, commission, remuneration, and interest, other than this, any other source of income is not eligible.
ITR-4 Form
This form is also known as Sugam. Individuals who run a business or other professions and accrue income from it can use this form. In this form, clubbing of income can be added from any windfall. Thus professionals like doctors, shopkeepers, designers, retailers, etc, can file their ITR using this form. Individuals whose income is raised from business or whose agriculture income is below Rs.5000 or an individual whose income is within India or he/she earns income through his/her single house property.
ITR-5 Form
This form is for business trusts, firms, etc. Partnership firms or LLPs are eligible to apply for ITR-5. Limited Liability Partnerships, Body of Individuals (BOIs), Association of Persons, and Investment Funds are eligible for this form. An individual who files in ITR-1, Hindu Undivided Family, Company, or any taxpayer's income arising from capital gains is not eligible for this form.
ITR-6 Form
ITR-6 is for the companies to file their Income Tax Returns but only in electronic mode. All companies can file ITR under this form, only the company claiming deductions under section 11 cannot file this form.
ITR-7 Form
When any individual or any company claims for furnishing the returns under sections 139(4A), 139(4C), 139(4D), 139(4E), or 139(4F) can file an ITR-7 form. Individual’s income arising from capital gains or whose income is through salary or Hindu Undivided family Under ITR 1 or bodies who are eligible for form ITR 5 cannot file under ITR 7 are not eligible for this form.
Documents for filing Income Tax Return
The documents required to file income tax returns are given below-
- Pan Card
- Aadhar Card
- Form 16
- Month-wise salary slips
- Form-16 A/ Form 16 B/ Form 16 C
- Bank account details
- Bank statement/ Passbook
- Investment Proofs
- Form 26AS
- Interest Income and other Interest Certificates
- Capital Gain from sale of property, mutual funds, shares
- Details of Investment in Unlisted Shares
- Home Loan Statement
- Rental Income
- Foreign income/ Dividend Income
Procedure for Income Tax Return Filing
Follow the steps given below for the purpose of Income Tax Return Filing-
Step 1: Calculation of Income and Tax
The taxpayers need to calculate/her income according to income tax law provisions. The income calculated must take into consideration all the sources i.e., salary, interest, dividend, etc.
Step 2: Tax Deduction at Sources Certificate and Form 26AS
Form 26AS is for taxpayers to summarise their TDS amount and tax paid during the assessment year. The taxpayer must check the TDS certificate for all four quarters of the financial year.
Step 3: Choose the Right Income Tax Form
The taxpayer needs to ascertain the income tax form which is applicable to him according to the categories prescribed. After ascertaining the form the taxpayer can start his proceedings for filing the same. For filing the return there are two modes available for taxpayers, they can choose wisely accordingly to their connivance via online mode or offline mode.
Step 4: Downward ITR Utility from Income Tax Portal
By visiting the site of the government Income Tax Return Filing Department and from the menu bar click on downloads. Select the assessment year from there and download the offline utility software.
Step 5: Fill all the Detail in the Form
After downloading the offline utility, fill up the required details of the income, and check the refund receivable as per the utility calculation. Income tax challan details can also be filled in the downloaded form.
Step 6: Validate the Information Entered
In the downloaded form, a few buttons could be seen on the right-hand side where the option for validation is shown. Click on the same to be ensuring that all the information required and filled in the form is true.
Step 7: Convert the file to XML Format
After successfully validating, tap on the ‘Generate XML’ button to convert the same into XML format.
Step 8: Upload the XML File to the Income Tax Portal
Next, log in to the income tax e-filing site and tap on the ‘e-file’ tab, and select the income tax return option. Upload all the necessary details in the portal i.e., PAN, ITR form number, assessment year, and the mode of submission. Now attach the XML file and press the submit button. Choose the verification modes available i.e., Aadhar OTP electronic verification code (EVC), or manually send a signed copy of ITR-V to CPC, Bangalore.
Penalty on late Income Tax Return Filing
The income tax return must be filed on time by every taxpayer. Delaying in the same would cost huge penalties to the taxpayer. The government has imposed some penalties for the same as mentioned below-
- According to section 234F of the income tax act, filing ITR after the due date passed would make the taxpayer pay a maximum of Rs.5000/-
- Rs 1000/- will be penalized if the total income of the taxpayer does not exceed Rs. 5 lakhs.
- If tax is filed after 31 December but on or before 31st March of the assessment year Rs. 10 thousand would be penalized.
Why BizAdvisors?
Following are the reasons one should choose BizAdvisors-
- Our clients can also keep track of the progress on our platform at any moment.
- Our knowledgeable professionals are here to answer any queries you have.
- We will make sure that your interactions with professionals are pleasant and smooth.
- We always try our best to make our clients happy with the legal services we provide.
- We provide free legal advice.
- Our prices are transparent and reasonable.
- We deliver your work on time.
- We have a team of experts.
- We give money back guarantees as well.
- 200+ CA and CS assisted us in our work.
- We give an option of easy and convenient EMIs
Income Tax Return filing is a crucial step for every assessee but to file the same before the due date is also important. It provides benefits that make every assessee file ITR. Also delay in filing makes a taxpayer pay a fine. Income Tax Return filing has made financial transactions accountable. And since it can be done online, it gives the advantage to the taxpayers to file it with ease
Frequently Asked Questions
Income Tax Return is a form that a person is supposed to submit to the income tax department. It contains information about the person’s income and the taxes to be paid on it during the year.
ITR-3: As a salaried employee, one can file an ITR-3 if he/she receives income from salary, business or profession, house property [one or multiple], capital gains, and other sources.
The government has imposed some penalties for the late Income Tax Return Filing as mentioned below-
- According to section 234F of the income tax act, filing ITR after the due date passed would make the taxpayer pay a maximum of Rs.5000/-
- Rs 1000/- will be penalized if the total income of the taxpayer does not exceed Rs. 5 lakhs.
- If tax is filed after 31 December but on or before 31st March of the assessment year Rs. 10 thousand would be penalized.
On the basis of residence, the assessees are divided into three categories as mentioned below-
- The Ordinary Resident
- Not Ordinary Resident
- Non Resident
 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325











